Travel Tips
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Search
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
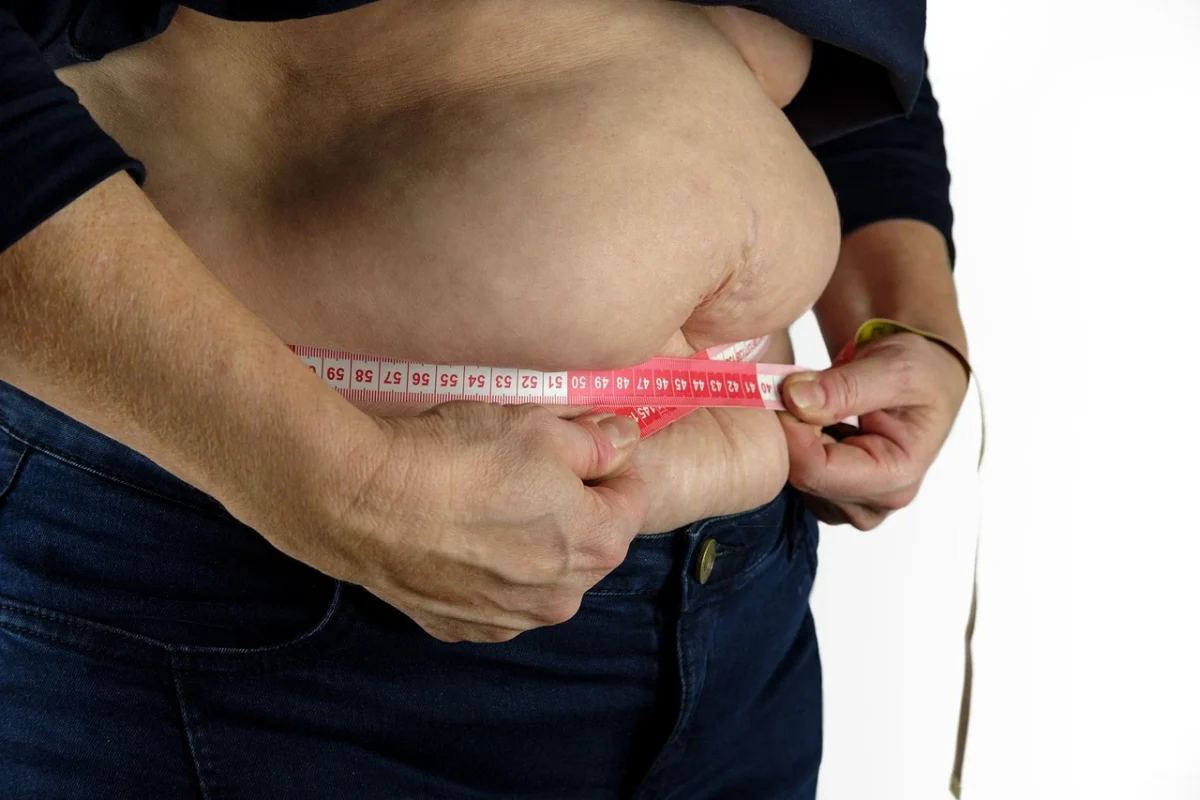
Men and obesity have become one of the most pressing global health concerns, with men being particularly vulnerable to its adverse effects. This multifaceted condition goes beyond aesthetics, affecting physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Understanding the specific ways obesity impacts men and the strategies available to combat it is crucial for improving health outcomes

Obesity in men leads to significant health risks, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. The biological and lifestyle factors unique to men often exacerbate these risks. Central obesity—excess fat stored around the abdomen—is especially dangerous, as it is linked to metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease.
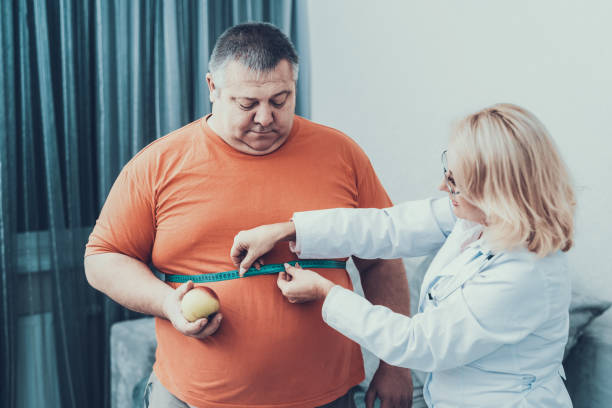

Men may ignore or downplay health symptoms, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Early warning signs include:
Many gyms and online platforms offer male-focused weight loss programs.
Virtual consultations with dietitians, personal trainers, and psychologists make accessing help easier.
Conclusion
Obesity is a complex health issue for men, influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors. Addressing it requires a holistic approach that combines education, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions. Early detection and proactive management can significantly improve health outcomes and enhance quality of life.
By understanding the unique challenges men face with obesity, healthcare providers, families, and individuals can work together to combat this growing epidemic effectively.
1. What is considered obesity in men?
Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. In men, abdominal obesity (a waist circumference greater than 40 inches) is a significant indicator of health risks.
2. Why is abdominal obesity particularly dangerous for men?
Abdominal fat, or visceral fat, surrounds vital organs and is associated with increased risks of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
3. Can low testosterone levels contribute to obesity in men?
Yes, low testosterone levels can lead to reduced muscle mass and increased fat storage, creating a cycle where obesity further lowers testosterone.
4. What is the best type of exercise for men with obesity?
A combination of aerobic exercises (e.g., walking, cycling) and strength training is most effective for weight loss and improving overall health.
5. Are weight loss medications safe for men?
FDA-approved weight loss medications can be safe when prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider. They are typically recommended for men with a BMI of 30 or higher or 27 with obesity-related health conditions.
6. How can men stay motivated to lose weight?
Setting realistic goals, tracking progress, and joining support groups or fitness communities can help maintain motivation. Partnering with a healthcare provider or coach also adds accountability.
Comments