Travel Tips
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Search
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
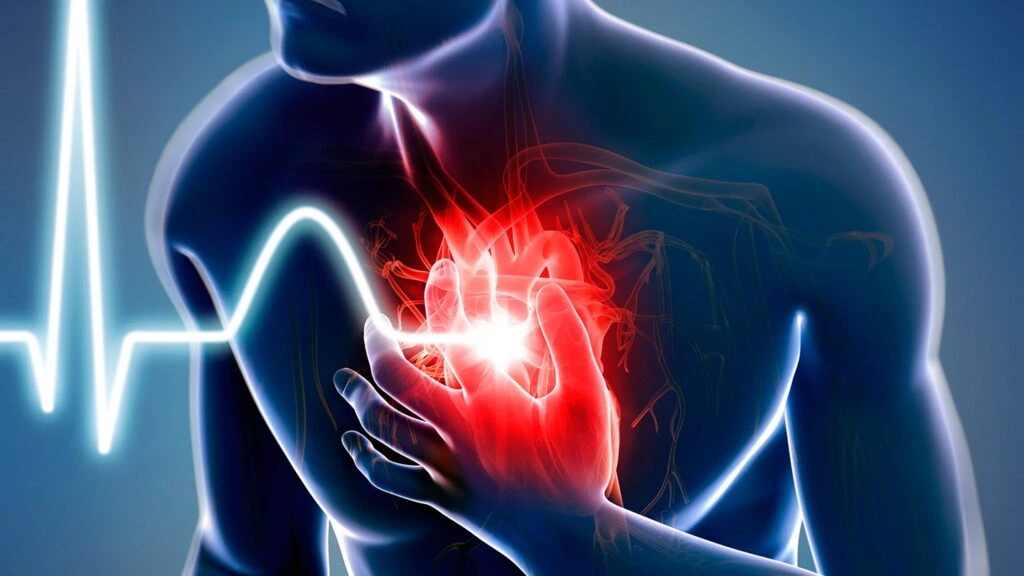
A heart attack, medically known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a section of the heart is obstructed, depriving the heart tissue of oxygen. This interruption can result in severe damage to the heart muscle. Knowing the causes, warning signs, and treatment options is vital for minimizing the impact of this condition and promoting prevention.
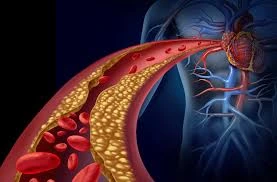
The leading cause of a t is the accumulation of plaque in the coronary arteries, a condition referred to as atherosclerosis. Plaque is a mix of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances that can block arteries. If this buildup ruptures, a blood clot can form and cut off the oxygen supply to the heart.
Other causes include:
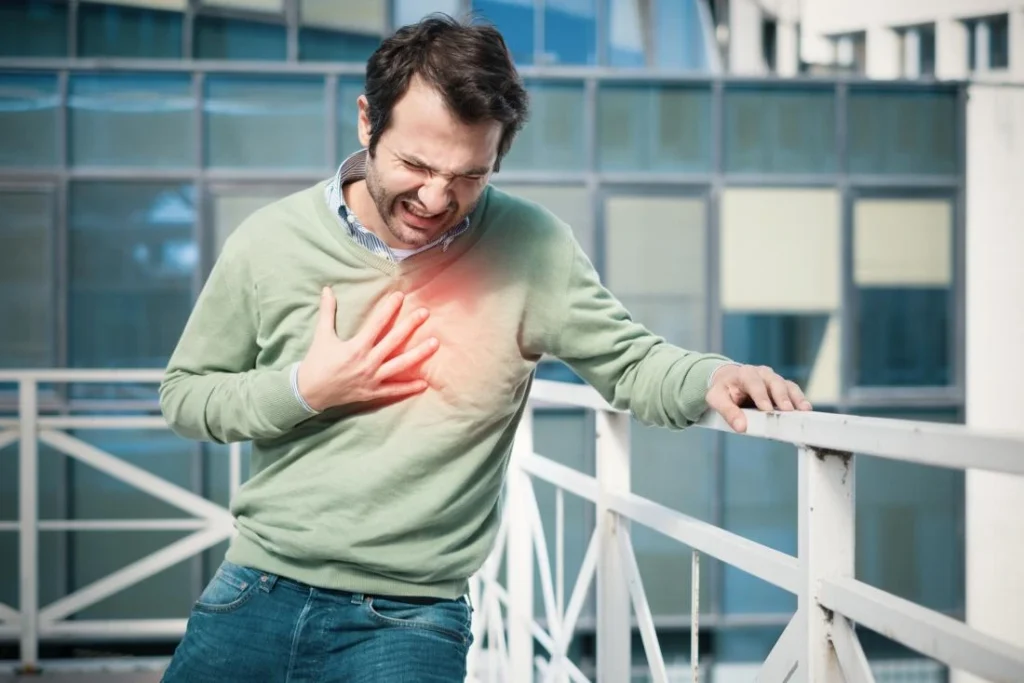

Symptoms can vary and are not always easily identified. Key warning signs include:
It’s crucial to seek medical help immediately if these symptoms occur, as early intervention can save lives.
Certain lifestyle factors and genetic predispositions increase vulnerability. Common contributors include:
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination and may include tests like an ECG, blood enzyme analysis, and imaging such as echocardiograms. If confirmed, treatments typically involve:
Though not all cases can be avoided, many risks are manageable through lifestyle choices:
Heart attacks are a critical health issue that demands swift action and informed prevention strategies. Recognizing symptoms, addressing risk factors, and embracing a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in protecting heart health. Stay proactive and prioritize regular check-ups to stay ahead of potential risks.
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a section of the heart is obstructed, causing damage to the heart muscle. This is most commonly due to plaque buildup in the coronary arteries.
Typical symptoms include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, pain in the arms, neck, or back, cold sweats, dizziness, nausea, and fatigue. Women may experience less classic symptoms, such as indigestion or extreme tiredness.
The primary cause is coronary artery blockage due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis). Plaque rupture can form a clot, further obstructing blood flow. Artery spasms or clotting disorders are other potential causes.
Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, inactivity, stress, and a family history of heart disease.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, an ECG to detect heart activity changes, blood tests for enzyme levels, and imaging tests like echocardiograms or angiograms to assess heart function and blood flow.
Treatment options include medications like aspirin, clot-dissolving drugs, and blood thinners, as well as procedures such as angioplasty (PCI), bypass surgery (CABG), and post-event cardiac rehabilitation.
Prevention focuses on a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, quitting smoking, stress management, and keeping blood pressure and cholesterol in check.
Recovery varies but typically includes a few weeks for light activity and several months for full recovery. Cardiac rehabilitation programs improve physical and emotional recovery.
While many heart attacks are preceded by symptoms like chest pain or nausea, some happen suddenly without obvious warning signs, especially in individuals with high risk factors.
Yes, with effective treatment, lifestyle changes, and ongoing care, many individuals go on to live healthy, active lives following a heart attack.
Comments