Travel Tips
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Search
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
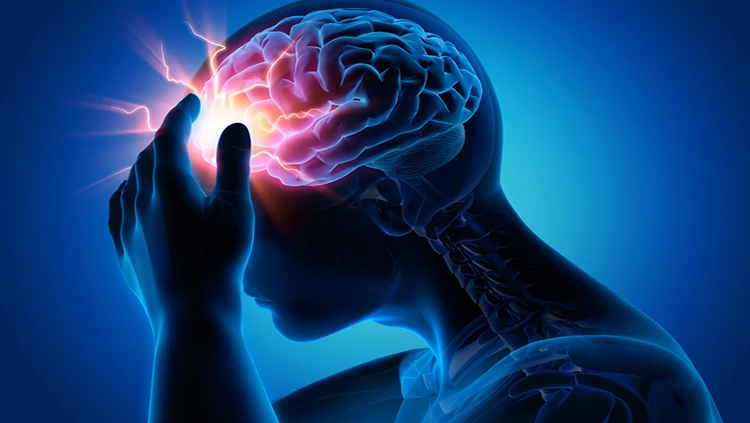
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a blow, bump, or jolt to the head or body that results in the brain moving rapidly back and forth. While often considered mild compared to other brain injuries, concussions can have serious consequences if not properly addressed.
When the brain experiences sudden movement, it can collide with the skull, leading to chemical changes or damage to brain cells. This disruption affects brain function temporarily, but repeated concussions or severe injuries can cause long-term effects.
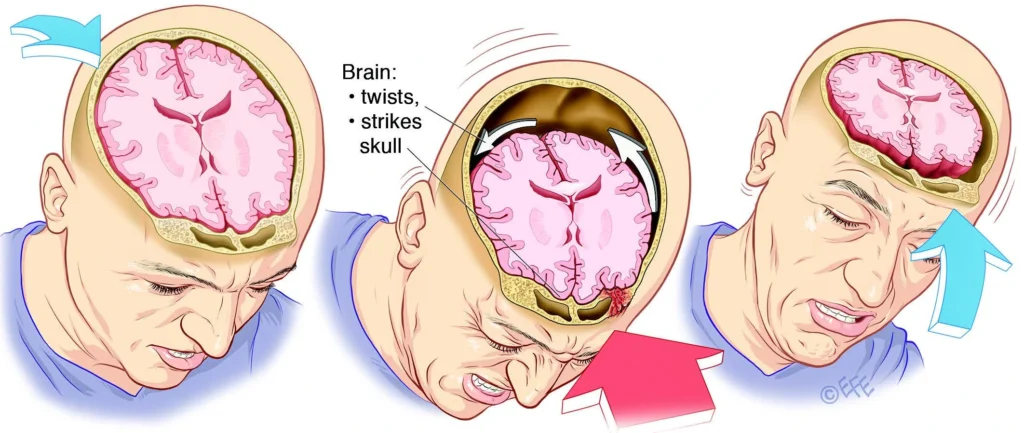
Concussions can result from various scenarios, including:
Symptoms may appear immediately or develop hours to days after the injury. Common signs include:
In some cases, severe symptoms like prolonged loss of consciousness, worsening headaches, or seizures require immediate medical attention.
A healthcare provider will evaluate the injury using:
Most concussions resolve with rest and proper care, but recovery varies based on severity and individual health. Key steps include:
For persistent symptoms, specialized rehabilitation or therapy may be necessary.
Ignoring a concussion can lead to complications like:
While not all concussions can be avoided, these steps can reduce the risk:
Seek immediate care if a concussion involves:
A concussion is not something to ignore, even if symptoms seem mild. Recognizing the signs, seeking proper care, and taking preventive measures can protect your brain health. Stay informed about concussion safety and recovery, and remember to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect an injury.
For more insights into health and wellness, visit LifePulseAI and empower yourself with knowledge.
1. What is a concussion?
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a direct impact to the head or a sudden jolt that affects normal brain function.
2. What causes concussions?
Common causes include sports injuries, falls, car accidents, workplace incidents, and physical assaults. Even indirect trauma, such as a sudden stop, can lead to a concussion.
3. What are the symptoms of a concussion?
Symptoms can include headache, confusion, dizziness, nausea, memory issues, sensitivity to light or sound, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
4. How is a concussion diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a clinical evaluation of symptoms, neurological tests, and possibly imaging tests like a CT scan or MRI to rule out more severe injuries.
5. How are concussions treated?
Treatment focuses on rest and symptom management. Cognitive and physical rest, avoiding screens and strenuous activities, and gradually returning to normal routines are key.
6. How long does it take to recover from a concussion?
Most people recover within 1-2 weeks, but some may experience symptoms for longer. Recovery times vary depending on the severity and individual factors.
7. Can you prevent a concussion?
While not all concussions can be prevented, wearing protective gear during sports, using seat belts, and creating safe environments can reduce risk.
8. Are children more susceptible to concussions?
Yes, children are more vulnerable due to their developing brains, and their symptoms may last longer than adults’. Special care is needed in diagnosing and treating concussions in children.
9. What is second impact syndrome?
Second impact syndrome occurs when a person sustains a second concussion before fully recovering from the first. This can lead to severe brain swelling and even death.
10. When should I see a doctor after a head injury?
Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen, such as severe headache, repeated vomiting, slurred speech, confusion, or loss of consciousness.
Comments