Travel Tips
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Search
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
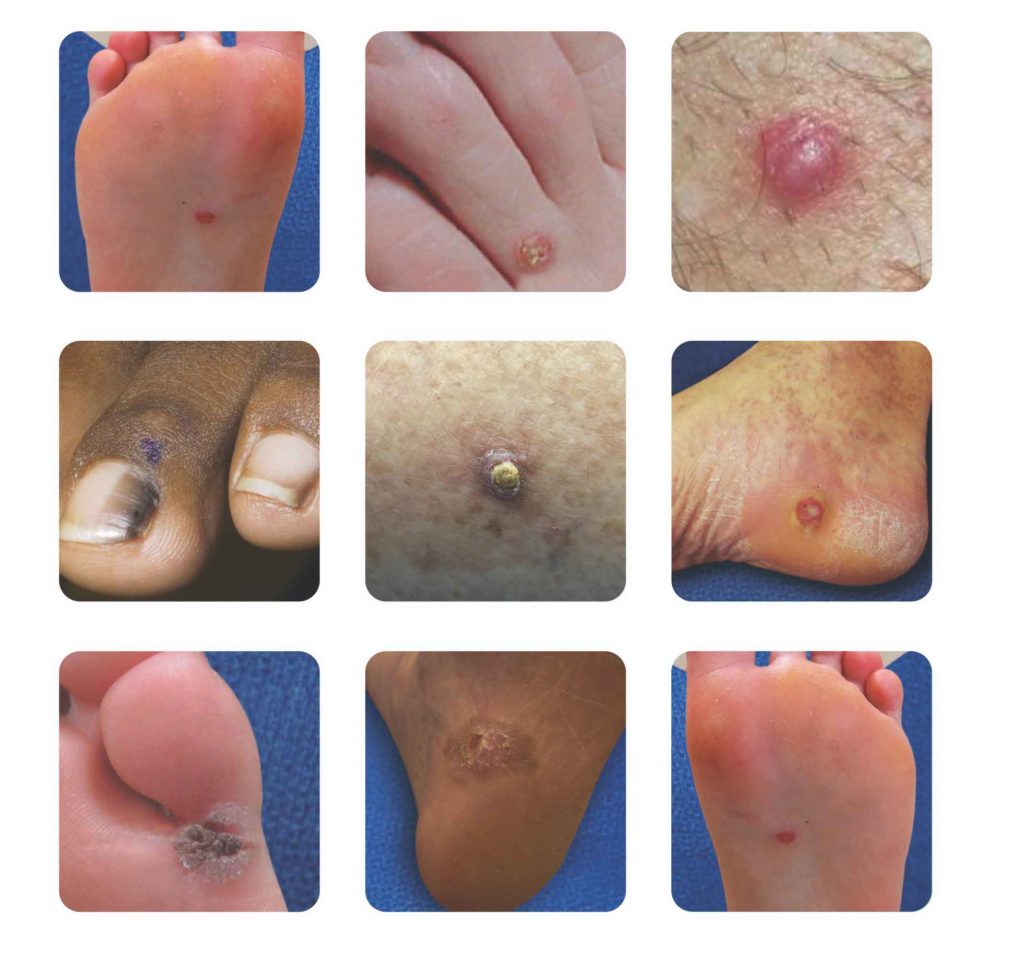
Foot cancer, while rare, is a significant health concern that can develop in the foot’s skin, bones, tendons, or soft tissues. Many people are familiar with common foot conditions like plantar fasciitis, but foot cancer often goes unnoticed because its symptoms can be subtle. Identifying and addressing the condition early is essential for better outcomes.
Foot cancer involves the growth of malignant tumors in the foot. These tumors can affect different parts of the foot, including:

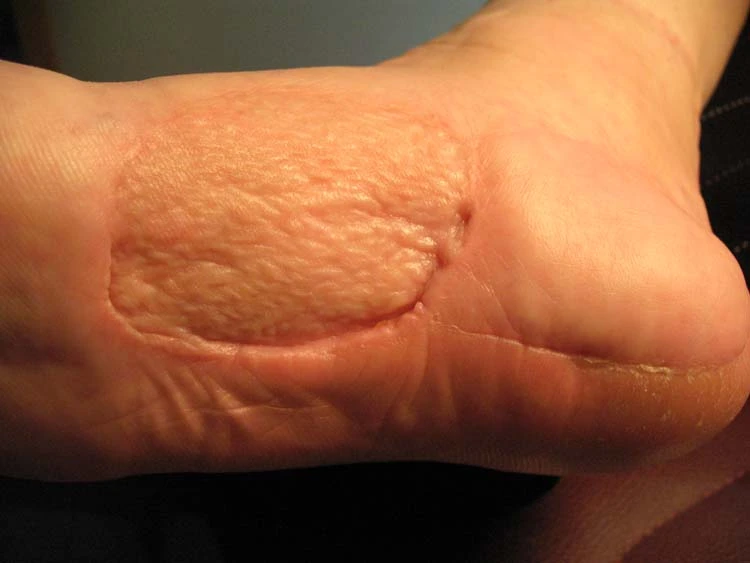
Symptoms of foot cancer can resemble other foot issues, making it challenging to detect. Be mindful of the following signs:
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience these symptoms, particularly if they persist or worsen over time.
Although foot cancer is uncommon, certain factors may elevate the risk:
Accurate diagnosis is crucial and may involve several methods:
The approach to treatment varies depending on the cancer type, stage, and location. Common methods include:
Surgical removal is the primary treatment. While some cases allow for limb-sparing surgery, advanced cancers may necessitate partial or full amputation.
This treatment uses high-energy rays to eliminate cancer cells and is often paired with surgery to improve outcomes.
Drugs are administered to slow the growth of cancer cells, particularly in advanced stages.
These modern therapies enhance the immune response or focus on cancer cell pathways to inhibit growth.
After surgery, physical therapy and counseling support recovery and quality of life.
While prevention isn’t always possible, you can take proactive measures:
The outlook for foot cancer depends on its type and the stage at which it is detected. Early intervention offers the best outcomes. Post-treatment care, including rehabilitation and regular follow-ups, is essential for maintaining well-being and functionality.
If you observe unexplained changes in your feet, such as persistent pain, swelling, or unusual skin lesions, don’t delay consulting a medical professional. Early diagnosis significantly improves treatment success rates.
Foot cancer, though rare, requires awareness and timely action. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers you to take control of your health. For more detailed insights on foot health and other wellness topics, visit LifePulseAI and stay proactive in safeguarding your well-being.
These refer to malignant tumors forming in the skin, bones, or soft tissues of the foot. They include skin cancers (e.g., melanoma), bone malignancies like osteosarcoma, and soft tissue sarcomas such as synovial sarcoma.
Cancers of the foot are rare compared to other types. However, they can often be misdiagnosed due to their similarity to common foot problems.
Symptoms include persistent lumps, non-healing sores, discoloration, changes in moles, unexplained pain, and difficulty walking.
Risk factors include excessive sun exposure, a family history of cancer, repeated injuries to the area, exposure to harmful chemicals, and a compromised immune system.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs, biopsies to analyze tissue samples, and blood tests to detect cancer markers.
Treatment depends on the type and stage of the cancer. Options include:
Early detection improves the likelihood of successful treatment. Advanced cases might need more extensive intervention, and outcomes depend on the stage at diagnosis.
While not all cases can be prevented, you can reduce risk by:
No, most abnormalities, like cysts or benign growths, are non-cancerous. However, persistent or unusual lumps should be examined by a healthcare provider.
Yes, a dermatologist, oncologist, or orthopedic surgeon can provide accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment for suspected cases of cancer in the foot.
Comments