Surgical Treatment of Obesity: Benefits and Options
Surgical Treatment of Obesity: A Comprehensive Guide
Obesity is a complex and multifaceted condition that poses serious risks to physical health and quality of life. While lifestyle interventions such as diet and exercise are essential for weight management, they may not be effective for everyone, particularly for those with severe obesity or obesity-related health conditions. In such cases, surgical treatment, also known as bariatric surgery, can be a life-changing option.
What Is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery refers to a group of procedures designed to aid significant weight loss by altering the digestive system. These surgeries are not quick fixes but rather tools that work in conjunction with lifestyle changes to help individuals achieve and maintain a healthier weight.
Who Is a Candidate for Bariatric Surgery?
Candidates typically meet the following criteria:
- A body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions (e.g., type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea).
- Inability to achieve sustainable weight loss through non-surgical methods.
- A commitment to long-term lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and physical activity.
Types of Bariatric Surgery
There are several types of bariatric surgery, each with unique benefits and risks:
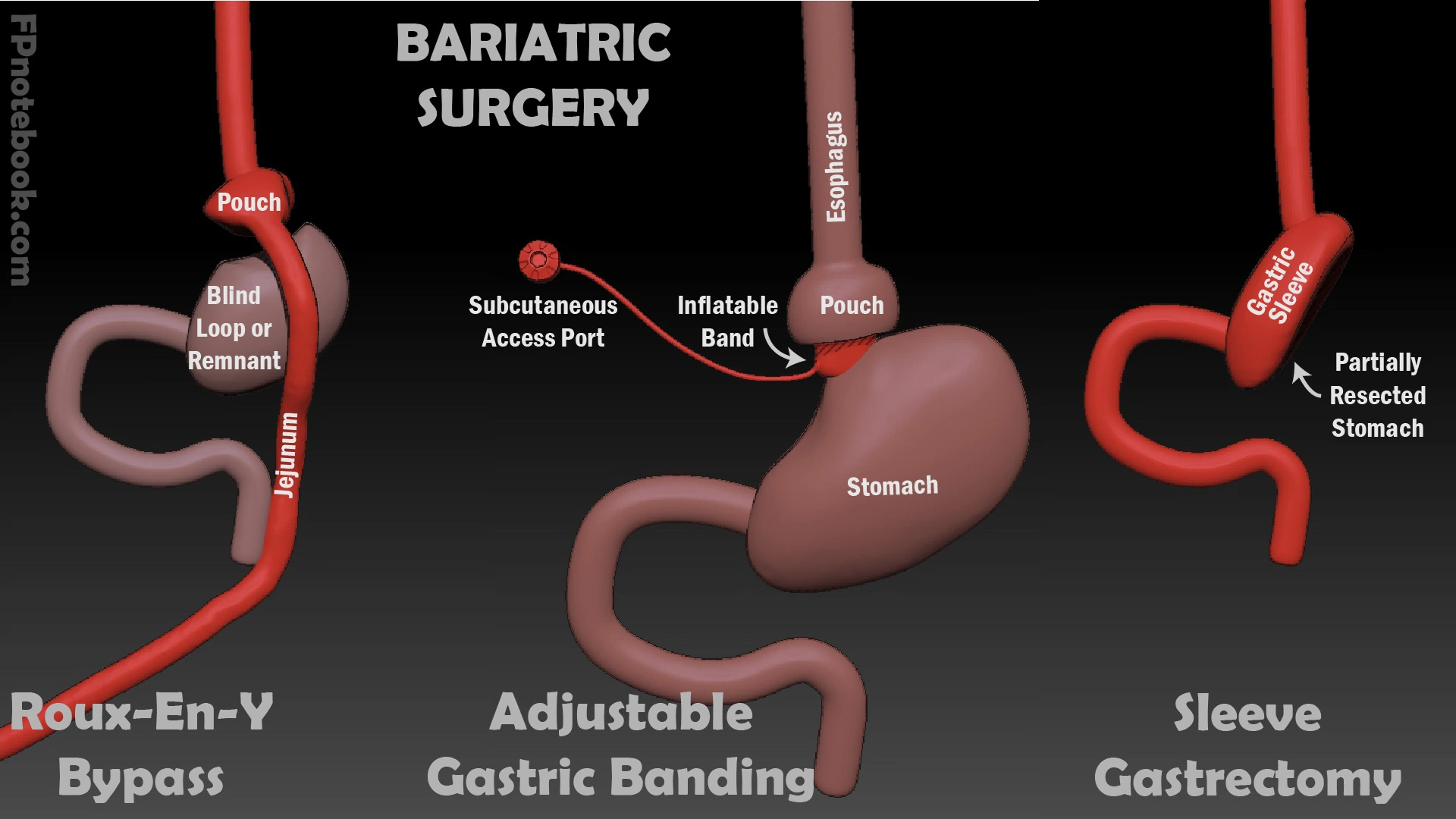
1. Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
This procedure involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine. This bypasses most of the stomach and a portion of the small intestine.
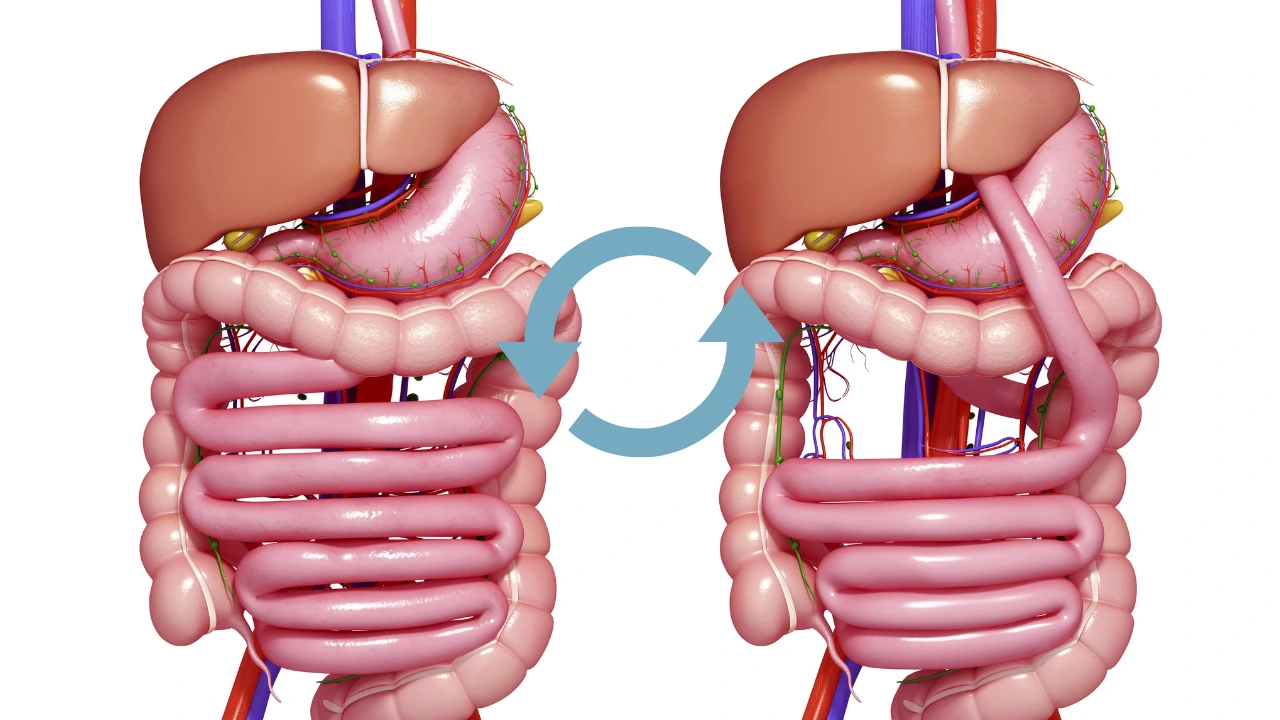
- Advantages: Significant and sustained weight loss; improvement in obesity-related conditions.
- Risks: Nutritional deficiencies; dumping syndrome (rapid emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine).
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy
In this procedure, approximately 80% of the stomach is removed, leaving a tube-shaped stomach or “sleeve.”
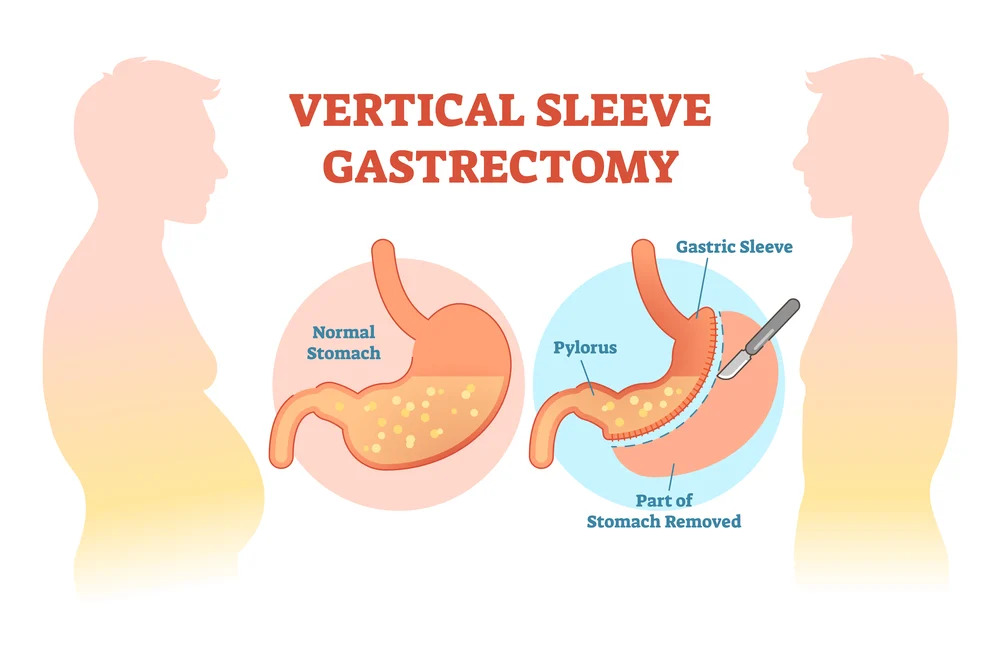
- Advantages: Fewer complications than gastric bypass; effective weight loss.
- Risks: Potential for acid reflux; irreversible.
3. Adjustable Gastric Banding
A silicone band is placed around the upper stomach to create a small pouch. The band can be tightened or loosened as needed.
- Advantages: Reversible; adjustable.
- Risks: Slower weight loss; potential for band slippage or erosion.
4. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
This procedure combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a bypass of a significant portion of the small intestine.
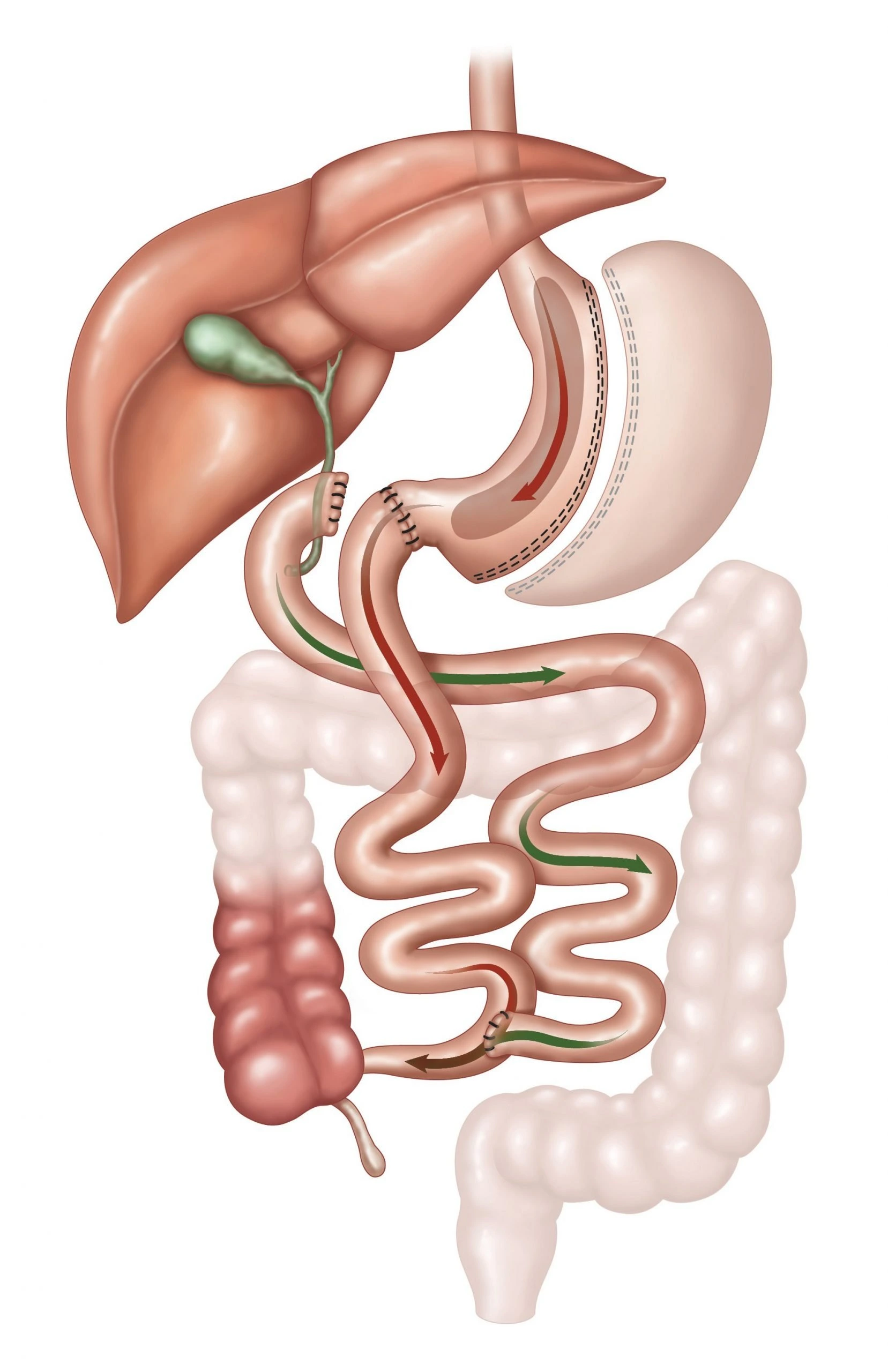
- Advantages: Greatest potential for weight loss; effective in resolving obesity-related conditions.
- Risks: Higher risk of nutritional deficiencies; complex surgery.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
- Significant Weight Loss: Most patients lose 50-70% of their excess weight within two years.
- Improvement or Resolution of Comorbidities: Conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea often improve or resolve.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Increased mobility, reduced joint pain, and improved mental health are common outcomes.
Risks and Considerations
Bariatric surgery carries risks, as with any surgical procedure. Potential complications include:
- Infection or bleeding.
- Nutritional deficiencies due to altered digestion and absorption.
- Psychological challenges, including adjusting to a new body image and coping with lifestyle changes.
Preparing for Surgery
Preparation involves a thorough evaluation, including medical, nutritional, and psychological assessments. Patients may need to follow a pre-surgery diet to reduce liver size and improve surgical safety.
Life After Bariatric Surgery
Post-surgery, patients must adopt significant lifestyle changes:
- Following a nutrient-dense, portion-controlled diet.
- Taking prescribed vitamin and mineral supplements.
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Attending follow-up appointments to monitor progress and address any complications.
Is Bariatric Surgery Right for You?
Deciding to undergo bariatric surgery is deeply personal and should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare team. It is essential to understand the potential benefits, risks, and commitment required to achieve long-term success.
Bariatric surgery offers hope for individuals struggling with severe obesity, but it is not a standalone solution. When combined with lifestyle changes, this powerful tool can pave the way toward a healthier and more fulfilling life.
If you’re considering bariatric surgery, talk to your doctor to determine the best approach for your unique needs.
FAQ: Surgical Treatment of Obesity
1. What is the recovery time for bariatric surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the procedure. Most patients stay in the hospital for 1-3 days and can resume normal activities within 4-6 weeks. However, it may take several months to fully adjust to dietary and lifestyle changes.
2. How much weight can I expect to lose?
Weight loss depends on the type of surgery and individual factors. On average:
- Gastric bypass: 60-70% of excess weight.
- Sleeve gastrectomy: 50-60% of excess weight.
- Adjustable gastric band: 40-50% of excess weight.
- BPD/DS: 70-80% of excess weight.
3. Will bariatric surgery cure my type 2 diabetes?
Many patients experience significant improvement or complete resolution of type 2 diabetes, especially after gastric bypass or BPD/DS. However, results vary, and ongoing medical care is essential.
4. Are there age limits for bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery is generally approved for adults aged 18-65. In some cases, it may be considered for adolescents with severe obesity or older adults, depending on overall health and risk factors.
5. What are the dietary restrictions after surgery?
Initially, patients follow a liquid diet, gradually progressing to pureed, soft, and then regular foods. Long-term dietary guidelines emphasize small, nutrient-dense meals, avoiding high-sugar and high-fat foods.
6. Can I have children after bariatric surgery?
Yes, but it is recommended to wait at least 12-18 months after surgery before becoming pregnant. This allows weight and nutrient levels to stabilize. Bariatric surgery may improve fertility in individuals with obesity-related infertility.
7. Will my insurance cover bariatric surgery?
Coverage varies by insurer and policy. Many insurance plans cover bariatric surgery if medical criteria are met. Consult your provider to determine eligibility and pre-authorization requirements.
References
- American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS)
https://asmbs.org
A trusted resource for information on bariatric surgery procedures, outcomes, and patient education.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
https://www.niddk.nih.gov
Comprehensive resources on obesity treatment, including surgical options and long-term care.
- Mayo Clinic
https://www.mayoclinic.org
Articles and guides on the risks, benefits, and recovery process of bariatric surgery.
- Cleveland Clinic
https://my.clevelandclinic.org
Expert information on different types of weight-loss surgeries and their impact on health.
- Obesity Action Coalition (OAC)
https://www.obesityaction.org
Patient-centered education and advocacy regarding obesity treatment, including surgical interventions.
-
November 25, 2024
0 Views
-




Comments